What is urinary incontinence?
Urinary incontinence is the accidental emission of urine. It can happen when you cough, laugh, sneeze or jog. Or you may have a sudden need to go to the bathroom, but you can not get there in time. Problems with bladder control are very common, especially among older adults. In general, they do not cause serious health problems, but they can cause embarrassment.
Incontinence can be a short-term problem caused by a urinary tract infection, a medication or constipation. It improves when you treat the problem that is causing it. But this topic focuses on continuous urinary incontinence.
There are two main types of urinary incontinence. Some women, especially older women, have both.
- Stress incontinence occurs when you sneeze, cough, laugh, jog, or do other things that put pressure on your bladder. This is the most common type of bladder control problem in women.
- Urge incontinence happens when you have a strong urge to urinate, but you can not get to the bathroom in time. This can happen even when the bladder only has a small amount of urine. It is possible that some women do not feel any warning signs before having an accidental loss of urine. Other women may have an involuntary loss of urine when they drink water or when they hear or touch running water. Overactive bladder is a type of urge incontinence. But not all people with overactive bladder have urine loss.
What causes urinary incontinence?
The problems of bladder control could be caused by:
- Weakness of the muscles in the lower part of the urinary tract.
- Problems or damage to the urinary tract or nerves that control urination.
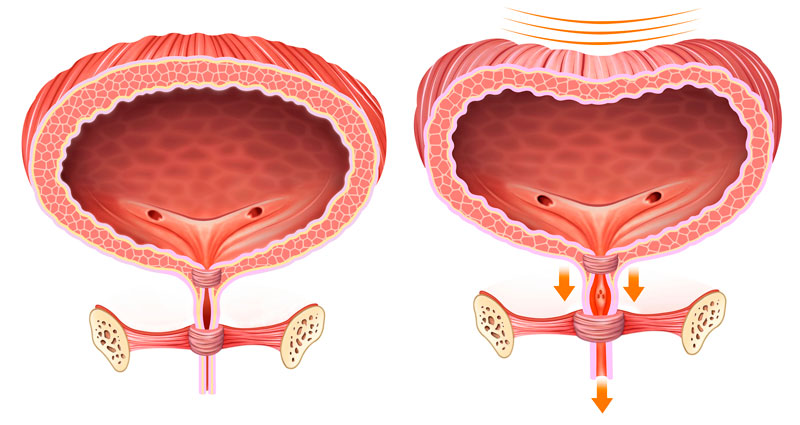
Stress incontinence can be caused by childbirth, weight gain or other conditions that stretch the pelvic floor muscles. When these muscles can not adequately hold the bladder, the bladder descends and puts pressure on the vagina. You can not contract the muscles that close the urethra. Then, an involuntary loss of urine may occur due to additional pressure on the bladder when you cough, sneeze, laugh, exercise or other activities.
Urge incontinence is caused by an overactive bladder muscle that pushes urine out of the bladder. It can be due to bladder irritation, emotional stress or brain conditions, such as Parkinson’s disease or a stroke. Many times, doctors do not know what the cause is.
What are the symptoms?
The main symptom of urinary incontinence is the accidental evacuation of urine.
- If you have stress incontinence, you may lose a small to medium amount of urine when you cough, sneeze, laugh, exercise, or similar things.
- If you have urge incontinence, you may feel an urgent and sudden need to urinate and the need to urinate frequently. With this type of bladder control problem, you may lose a greater amount of urine that can moisten your clothes or run down your legs.
- If you have mixed incontinence, you may have symptoms of both problems.
How is urinary incontinence diagnosed?
Your doctor will ask you what and how much you drink. It will also ask about the frequency and amount of urine and involuntary losses. It may help to keep track of these factors by using a bladder diary for 3 or 4 days before consulting your doctor.
Your doctor will examine you and may perform some simple tests to look for the cause of the bladder control problem. If your doctor thinks it could be caused by more than one problem, it is likely that he will do more tests.
How is it treated?
The treatments are different for each person. They depend on the type of incontinence you have and how much it affects your life. Once your doctor knows the cause of the incontinence, your treatment may include exercises, bladder training, medications, a pessary or a combination of these. Some women may need surgery. “Click here”
There are also some steps you can take at home. In many cases, these changes in lifestyle may be enough to control incontinence.
- Reduce your intake of caffeinated beverages, such as coffee and tea. Also reduce the consumption of effervescent drinks such as soft drinks. And do not drink more than one alcoholic beverage a day.
- Eat foods high in fiber to help prevent constipation.
- Do not smoke. If you need help to stop using tobacco, talk with your doctor about smoking cessation programs and medications. These can increase your chances of kicking the habit forever.
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Try simple exercises for the pelvic floor, such as Kegel exercises.
- Go to the bathroom several times a day at set times and wear clothes that can be easily removed. Keep the path to the bathroom as clear and short as you can.
- Keep a record of your symptoms and your accidental urine evacuations with a bladder diary. This can help you and your doctor find the best treatment for you.
- If you have symptoms of urinary incontinence, do not feel embarrassed to tell your doctor. Most people with incontinence can get help or be cured.
How can you prevent urinary incontinence?
Strengthening the pelvic muscles with Kegel exercises could reduce the risk of incontinence.
If you smoke, try to stop doing it. Quitting smoking could make you cough less, which could help with incontinence.
This information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Healthwise, Incorporated, disclaims all warranties and liability for the use of this information. Your use of this information implies that you accept the Terms of Use. Learn how we develop our content.
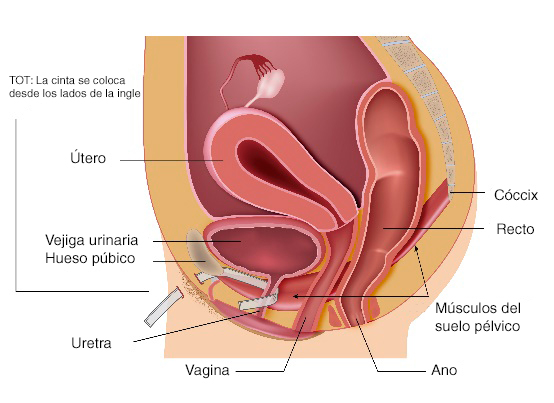
TVT and TOT surgical techniques for the correction of stress urinary incontinence:
The tension-free vaginal band (TVT) and transobturator tape (TOT) procedures are designed to lift the bladder or urethra to the normal position. During surgery, a narrow band of synthetic mesh is placed under the urethra. The band supports the urethra and the bladder like a hammock.
Why do I need this TVT or TOT procedure?
Your doctor may recommend a TVT or TOT procedure to treat stress urinary incontinence. Urinary stress incontinence is when pressure from an activity such as coughing, sneezing, laughing, running or lifting causes you to lose urine. The loss stops when the activity stops.
Stress urinary incontinence is quite common among women. It is caused by a weakness in the muscles and tissues that surround the bladder and urethra. Weakness prevents the urethra from closing, so urine escapes. TVT or TOT support can often alleviate or correct this problem.
How is the TVT or TOT procedure done?
The key difference between a TVT procedure and a TOT procedure is the way in which the surgeon reaches the urethra to place the tape.
TVT
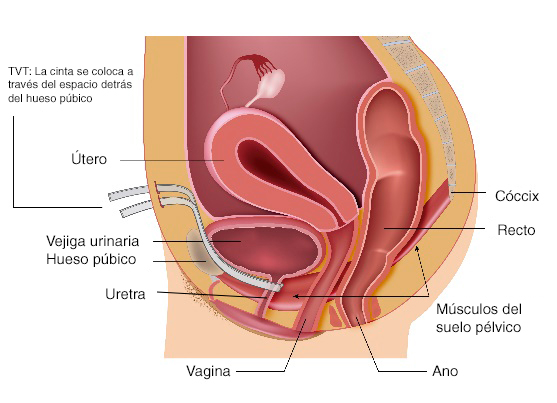
TOT